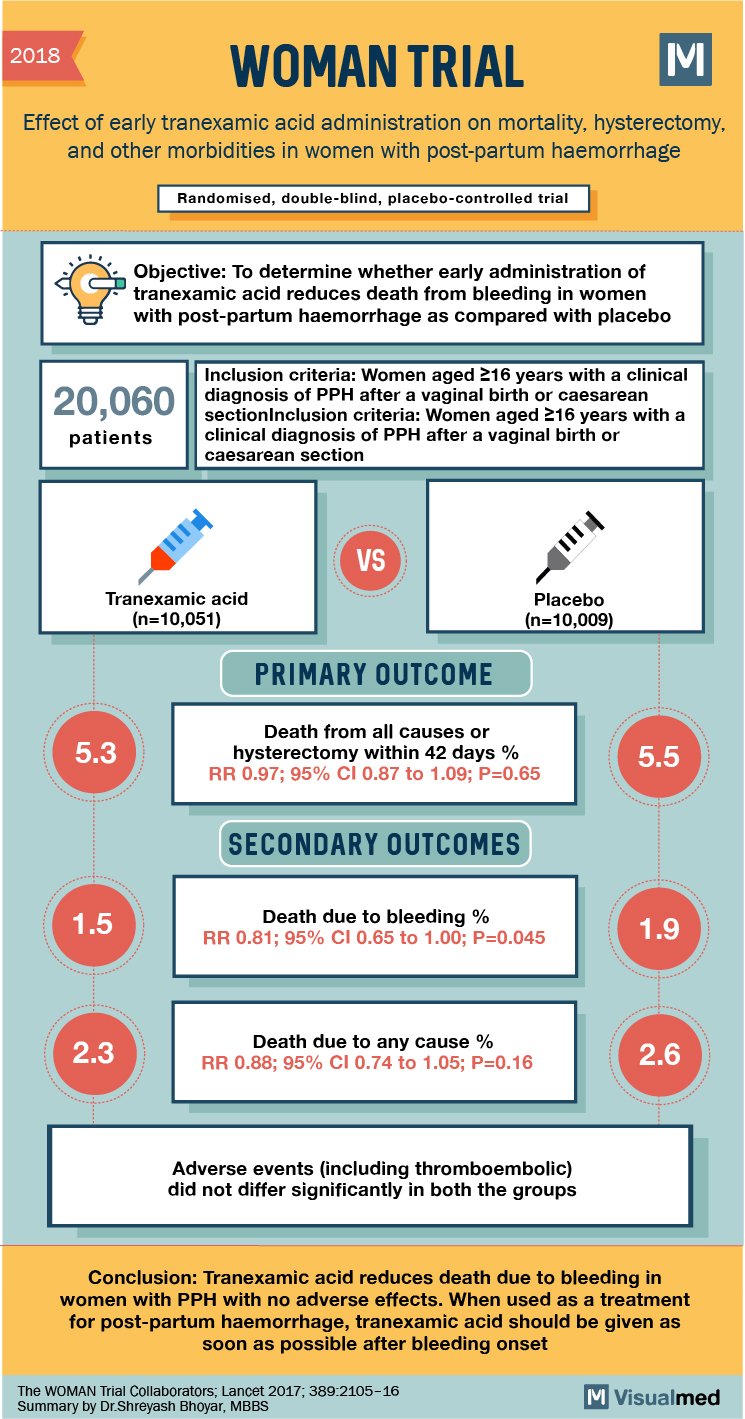
2018 WOMAN TRIAL Effect of early tranexamic acid administration on mortality, hysterectomy, and other morbidities in women with post-partum haemorrhage Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial Objective: To determine whether early administration of tranexamic acid reduces death from bleeding in women with post-partum haemorrhage as compared with placebo 5 20,060 Inclusion criteria: Women aged 216 years with a clinical diagnosis of PPH after a vaginal birth or caesarean section Inclusion criteria: Women aged 16 years with a clinical diagnosis of PPH after a vaginal birth or caesarean section patients Tranexamic acid (n=10,051) Placebo (n=10,009) PRIMARY OUTCOME 5.3 Death from all causes or hysterectomy within 42 days % RR 0.97; 95% CI 0.87 to 1.09; P=0.65 5.5 SECONDARY OUTCOMES 1.5 Death due to bleeding % RR 0.81; 95% CI 0.65 to 1.00; P=0.045 1.9 2.3 Death due to any cause % RR 0.88; 95% CI 0.74 to 1.05; P=0.16 2.6 Adverse events (including thromboembolic) did not differ significantly in both the groups Conclusion: Tranexamic acid reduces death due to bleeding in women with PPH with no adverse effects. When used as a treatment for post-partum haemorrhage, tranexamic acid should be given as soon as possible after bleeding onset The WOMAN Trial Collaborators; Lancet 2017; 389:2105-16