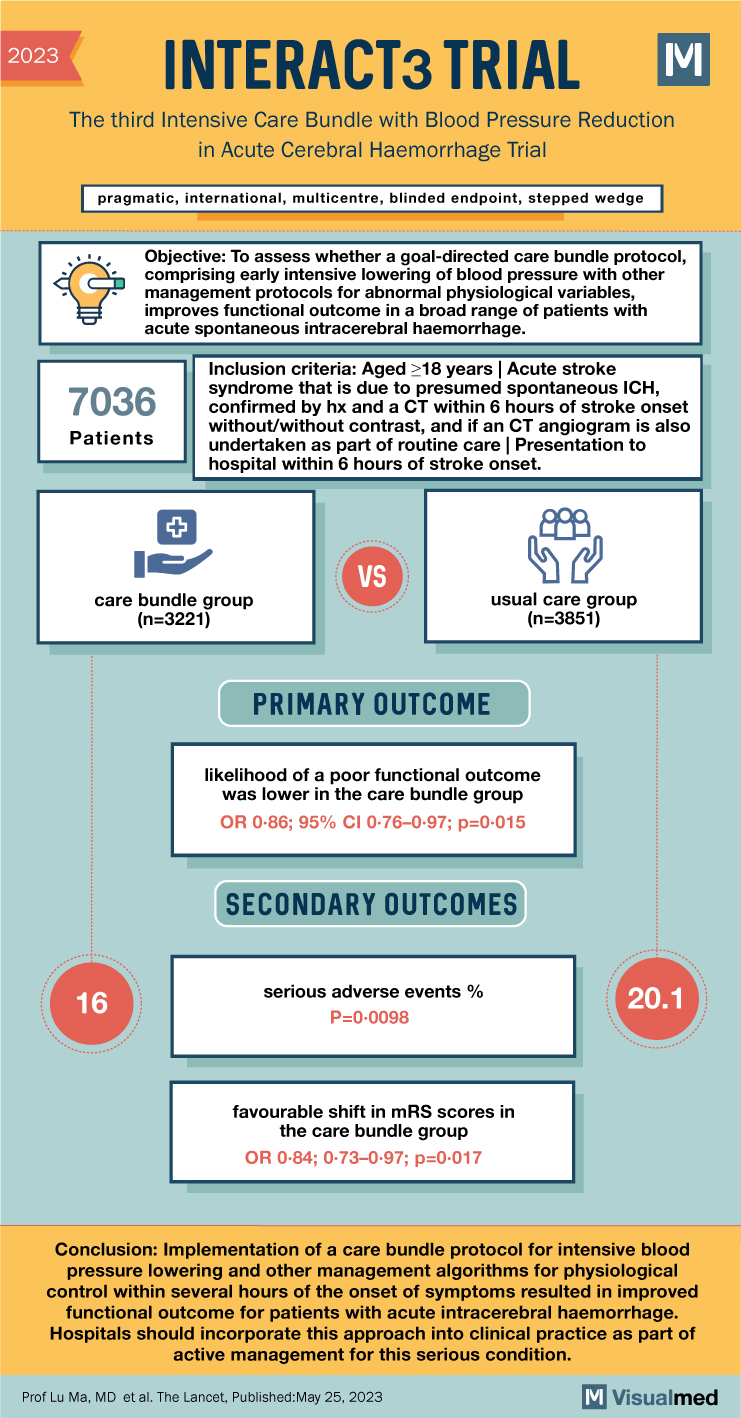
INTERACT3 Trial Summary
Background:
- Early control of elevated blood pressure is crucial for acute intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) treatment.
- The INTERACT 3 trial aimed to assess the impact of a goal-directed care bundle on outcomes for patients with acute spontaneous ICH.
- The care bundle included protocols for early intensive blood pressure lowering and management algorithms for hyperglycemia, pyrexia, and abnormal anticoagulation.
Methods:
- Pragmatic, international, multicenter, blinded endpoint, stepped wedge cluster randomized controlled trial.
- Conducted in nine low-income and middle-income countries and one high-income country.
- Hospitals eligible if they lacked consistent ICH-specific protocols and were willing to implement the care bundle.
- Patients aged ≥18 years with imaging-confirmed spontaneous ICH within 6 hours of symptom onset included.
- Exclusion criteria: Secondary ICH due to structural abnormalities, previous thrombolysis, or anticipated non-adherence.
Findings:
- 144 hospitals in ten countries participated, with 22 withdrawals before patient enrollment.
- 10,857 patients screened, with 3,821 excluded.
- Modified intention-to-treat population: 7,036 patients enrolled at 121 hospitals.
- Care bundle group: 3,221 patients; Usual care group: 3,815 patients.
- Primary outcome data available for 2,892 patients in the care bundle group and 3,363 patients in the usual care group.
Primary Outcome:
- Likelihood of poor functional outcome lower in care bundle group (common odds ratio 0.86; 95% CI 0.76-0.97; p=0.015).
- Favourable shift in modified Rankin scale (mRS) scores observed in the care bundle group across sensitivity analyses.
- Patients in the care bundle group had fewer serious adverse events compared to the usual care group (16.0% vs. 20.1%; p=0.0098).
Interpretation:
- Implementation of the care bundle protocol for early intensive blood pressure lowering and other management algorithms resulted in improved functional outcomes for acute ICH patients.
- Hospitals are encouraged to incorporate this approach into clinical practice as part of active management for acute ICH.
Trial Information:
- Registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03209258) and the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR-IOC-17011787).
- Trial completed, providing robust evidence for the efficacy of the care bundle approach in acute ICH management.
Key Takeaways:
- Early control of elevated blood pressure is crucial for acute intracerebral hemorrhage treatment.
- Implementing a care bundle protocol improved functional outcomes for patients with acute spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage.
- The care bundle included protocols for early intensive blood pressure lowering and management algorithms for hyperglycemia, pyrexia, and abnormal anticoagulation.
- Hospitals should consider incorporating this approach into their clinical practice to enhance management of acute intracerebral hemorrhage.